Pediatric Dentistry (Pedodontics)
The treatments performed in our clinic about Pediatric Dentistry (Pedodontics) are as follows. Please click here for the details of the treatments.

What is Pedodontics? Who is a Pedodontist?
What is Pedodontics?
Pedodontics or Pediatric dentistry is a department that covers childhood and adolescence starting from infancy and offers preventive and therapeutic treatments to prevent caries formation with early diagnosis of caries, trauma, orthodontic problems in milk and permanent teeth.
Who is a Pedodontist?
Pedodontist or pediatric dentist is a dentist who, following a 5-year undergraduate education in dentistry, has received expertise or doctoral training in the department of pedodontics affiliated to the faculty of dentistry on milk and permanent teeth, jaw and facial development, all protective and therapeutic applications according to need, as well as child psychology and approach to the child.
Why Are Milk Teeth Important?
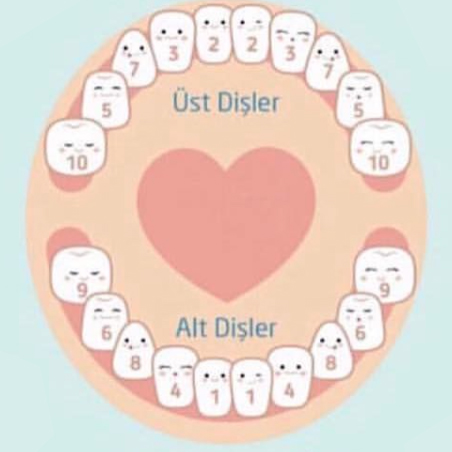
The period of milk dentition begins with the appearance of the first milk tooth in the mouth when the baby is approximately 6 months old, and is completed with the appearance of all milk teeth in the mouth between the ages of 2.5-3 years.
When the eruption of the milk teeth is completed, there are a total of 20 teeth, 10 teeth in the lower and upper jaw. You can examine the order of eruption of milk teeth in the table below.

Since the milk teeth will be completely changed, the problems that occur in these teeth are not taken seriously by the parents cause undesirable consequences for the future. These are
- Abscess formation due to deep caries,
- Premature extraction of teeth and related crowding,
- Speech sounds cannot be made correctly,
- Decay of anterior upper incisors due to early childhood caries (ECC) and aesthetic concerns
- In early childhood, due to the presence of too much caries, it can be listed as having to be treated under sedation or general anesthesia.
When Should the First Inspection Be Done?
It is recommended that the first visit to the dentist be made when the first tooth begins to erupt (6th month) or at the latest at the age of 1 year.
In addition, although the control period varies according to the caries risk status of the child, if the child does not have any general health and oral and dental health problems, the frequency of dental control should be 1 in 6 months.
Dental Caries in Children
Studies conducted in children aged 2-15 years in Turkey* show that the incidence of tooth decay varies between 43.5-84.9%.
This indicates that tooth decay is one of the most common chronic infections in childhood, that is, an important public health problem.
Therefore, early diagnosis, preventive practices such as fissure and fluoride, oral hygiene education, the role of parents (regulation of nutritional habits, acquisition of oral hygiene habits) are of great importance in reducing the incidence of tooth decay in our country.
*The frequency of tooth decay in primary school children of Büyükçekmece district of Istanbul. IU Dentist. Hek. Fak. Derg 1998; 32(1): 16-21 Akıncı T, Aktör O, Sepet E, Oray H, Sağlam E, Burmabıyıkoğlu S, Metin A, Kumbasar I, Bakırgil J, Bilgin B, Selvi S, Yılmaz S 33-39
Preventive Dentistry
Fissure Sealants (Tooth Shield)
The application of fissure sealant in children is a preventive dental treatment in which the grooves and indentations suitable for decay on the chewing surfaces of the molars are covered with a fluid filling material.
The goal of this preventive treatment is to prevent the accumulation of food residues and bacterial plaque in the grooves and recesses on the teeth and to make them easier to clean.
There is no loss of any substance in the tooth during the application. It is a one-session procedure. It is checked in routine examinations every 6 months.
Fluoride Application
When fluoride is used properly, it is a very safe and effective method both in preventing tooth decay and in controlling tooth decay. In the U.S. and other economically developed countries, the prevalence of fluoride use has been a major factor in the decline in the severity of tooth decay. (AAPD, American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, 2014)
Is it topical Fluorine? Is it Systemic Fluorine?
Since the systemic effect of fluoride on the teeth is neutralized by the eruption of the teeth, fluoride is applied topically today. The purpose of topical fluoride application is to prevent and delay the formation of caries in the tooth enamel. In the first 4 years when the teeth begin to appear in the oral environment, the enamel of the teeth is not mature, so fluoride application makes the structure of the teeth stronger and protects against caries attacks.
In what ways is topical Fluoride applied?
It can be applied in 2 ways, individual and professional.
Individual applications have been developed as daily agents containing low concentrations of fluoride, such as mouthwash, toothpaste, dental floss.
Professional applications containing high doses of fluoride in the form of varnish (varnish), gel, foam are applied only by dentists every 6 months on average. The frequency of application may vary according to the patient’s oral hygiene and diet.
Fluoride varnish is the application of fluoride with the consistency of cream to the teeth with the help of a special brush after the teeth are dried.
After the teeth are dried, fluoride in gel form is applied to the teeth for 1-4 minutes with the help of special carrier spoons.
What should be considered after fluoride application?
After fluoride application, nothing should be eaten or drunk for at least 1 hour. Teeth should not be brushed in the evening of application.
Is fluoride harmful?
It is impossible for your child to brush their teeth with fluoride toothpaste or to reach toxic doses by applying fluoride varnish/gel. In order for fluoride to have effects on the digestive system, a child weighing approximately 10 kg needs to swallow 45 g of paste (one tube of adult paste – approximately 1-5 mg/kg).
To avoid the unwanted effects of fluorine, make sure your child uses the right paste and make sure your child does not swallow the paste.
You can learn the appropriate paste for your child by consulting your physician.
The European Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (EAPD) has updated its Guidelines “The Use of Fluorine in the Prevention of Dental Caries in Children” in 2019. As in the rest of the world, the concentrations and amounts of fluoridated toothpaste recommended for use in children according to age in our country are given in the table below:

 http://www.tdb.org.tr/ekler/Florur_Durum_Raporu_2019.pdfhttps://www.eapd.eu/uploads/files/EAPD_Fluoride_Guidelines_2019.pdf https://www.aapd.org/media/Policies_Guidelines/BP_FluorideTherapy.pdf
http://www.tdb.org.tr/ekler/Florur_Durum_Raporu_2019.pdfhttps://www.eapd.eu/uploads/files/EAPD_Fluoride_Guidelines_2019.pdf https://www.aapd.org/media/Policies_Guidelines/BP_FluorideTherapy.pdf
Placeholders
One of the most important tasks of milk teeth is to protect the location of the permanent teeth that will come from below and to ensure their correct positioning.
While milk teeth, like permanent teeth, can be treated when decay occurs, they may need to be extracted in the presence of advanced infection.
When the milk teeth are extracted prematurely, the adjacent teeth begin to move towards the extraction cavity. In this case, when it is time for the permanent tooth at the bottom to come out, it will not find a place and cause crowding.
With the placeholder application, space loss and forward-looking orthodontic needs can be prevented.
Depending on the number of tooth losses, fixed or movable placeholders can be used.
Bad Mouth Habits
Finger sucking, pacifier sucking, lip or tongue sucking, nail biting, bruxism (teeth clenching and grinding), oral breathing are such habits.
Depending on the frequency and severity of these habits and the age of the child,
- abnormality in the development of the jaw-facial bones,
- transformation of the upper jaw tooth arch into a V-shape,
- Open closing,
- Cross closing,
- Speech and aesthetic disorders
- Change in the way of swallowing,
- Changes are observed in eruption and the position of the teeth.
!It is recommended to leave these habits until the age of 2.5 at the latest so that they do not damage the mouth and tooth structures.
Trauma
Dental trauma is one of the most common health problems in children after caries. It is more common in children between the ages of 1-3 who are young people and 7-10 years old, which is the school age period.
If there are general health problems such as bleeding, loss of consciousness, vomiting, nausea in post-traumatic children, the emergency department should be consulted as soon as possible.
If the child’s general condition is good, he should be examined by a pedodontist as soon as possible.
The first 1 hour after trauma is very important for the success of treatment.
What is important in broken teeth is the size of the broken part. If the broken part is too small, you should not waste time trying to find it, the solution should be done with filling. If a large part is broken, you can try to find the part and take it to the dentist.
If the tooth is completely dislodged, if possible, it should be washed under running water without touching the root part of the tooth and then kept in milk or saliva under the tongue and delivered to the dentist as soon as possible.
If your child is doing sports where there is a high probability of trauma to the mouth area, he should use a sports mouthguard to prevent dental traumas and soft tissue traumas that may occur in the mouth due to teeth.
! The International Society of Dental Traumatology (IADT) has developed an app to provide basic information about trauma. The application is free and has a Turkish language preference. When you click on the For Patients section, you can access images and information about what you can do after trauma. You can save the smiles of many children by downloading this app and sharing it with teachers, coaches and other parents.
Dental Treatment with General Anesthesia in Children
Although dental treatments can be performed under local anesthesia with behavioral guidance in most young children, children who cannot tolerate treatment due to excessive fear and anxiety, who need a lot of dental procedures, who require major surgical procedures, who have severe nausea reflexes, and who have mental and/or physical disabilities can often be treated under general anesthesia. All procedures from the treatment of decayed teeth to protective applications are carried out in a single session. Especially the risk of injury that may occur with the sudden movements of young children during treatment is eliminated.
After it is decided that the dental treatment will be performed under general anesthesia, the child is examined by the general anesthesiologist and the analyzes are evaluated and it is checked whether there is any risk under anesthesia.
The application of general anesthesia is carried out by the team work of the dentist and the anesthesiologist in a full-fledged hospital environment.
The duration of the procedure is determined by planning before the treatment and the family is informed about this issue. When the child is with his family without surgery, a calming syrup is given to him to relax. In this way, the child, who is woken up after all his treatment is completed and brought to his family in a short time, does not feel and does not remember that he has left. After being under observation for 1-2 hours after the procedure, he can go home on the same day.
In the post-treatment period, dental controls are carried out at regular intervals and the child’s oral hygiene is evaluated by the physician. With easily applicable protective applications, the formation of new caries is prevented and at the same time their concerns are reduced. It is very important for families to take an active role in proper and effective brushing and pay attention to the diet.
Doğal Dental Clinic - Other Treatments

Aesthetic Dentistry
Smile Design, Laminate Veneer (Leaf Porcelain), Zirconium Applications, Full Ceramic Crowns and Bridges, Composite Veneers (Bonding Applications), Teeth Whitening (Bleaching)

Orthodontics
Fixed Orthodontic Treatment, Removable Apparatus, Transparent Plaques (Wireless Orthodontic Treatment-Invisalign Technique)